Meiosis Definition
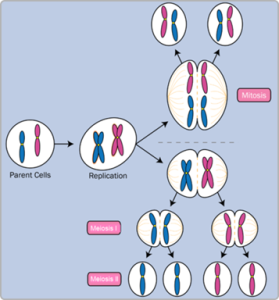
In meiosis, the number of chromosomes in a cell is halved.
The daughter cells receive only one chromosome from each pair of chromosomes.
So, chromosomes, which occur naturally in pairs, are separated from their other half during meiosis.
Meiosis – The Essential Principal
The essential principal of meiosis is that it consists of two divisions of the cell nucleus, resulting in four cells that contain only one individual chromosome.
Unlike mitosis, the new cells do not contain pairs of chromosomes.
So, after meiosis is complete, each cell consists of only half of the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
Meiosis and Fertilization
Meiosis occurs in the formation of sex cells.
These sex cells are called gametes.
A gamete is a cell that cannot develop any further unless it unites with another cell.
Eggs and sperm are two examples of gametes
During fertilization, the nuclei of the gametes combine.
If gametes were formed by mitosis instead of meiosis, the amount of chromosomes would double with each succeeding generation.
Meiosis insures that the correct amount of chromosomes are maintained during the fertilization process.
Meiosis I and II
Meiosis actually consists of two successive divisions.
First of all, the parent cell splits in two. During the first meiotic division, the chromosomes line up together.
After the chromosomes line up, they separate and go to different cells.
During the second meiotic division, the products of the first division split into two again.
So, after the second meiotic division, there are a total of four daughter cells.
Each of the daughter cells is genetically different.
No DNA replication occurs between the first and second meiotic division.
Therefore, meiotic division encourages genetic variation.
Haploid Cells
After meiotic division, each daughter cell is a haploid cell.
As opposed to the diploid cells that are formed in mitosis, the chromosomes in haploid cells do not have a partner of the same identical length and of the exact same genetic material.
In other words, a haploid cell has only one chromosome.
This single chromosome is half of the original chromosome pair.
So, each chromosome is unique in a haploid cell.
The Eight Stages
The stages of meiotic division are similar to those of mitosis.
Prophase I – The chromosomes become elongated strands before the chromosomes begin to pair.
Metaphase I – The envelope that contains the nucleus disappears and the chromosomes begin to line up at the equator of the cell.
Anaphase I – The chromosomes move towards the opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase I – Chromosome movement is complete. Two new cells are formed.
Prophase II – The chromosomes, which consist of members of each pair, condense.
Metaphase II – Chromosome align in the center of each spindle.
Anaphase II – The two chromatids of each pair move to opposite ends of the cells.
Telophase II – Four haploid cells are formed, each containing a haploid nucleus.
Only one of these four products develops into a functional cell.
The other three cells disintegrate.
The cell that survives contains only half of the pair of chromosomes from the original cell.
The complete process of meiotic division can take several days or even weeks.
Compare and Contrast Meiosis and Mitosis
Similarities
Both processes refer to cell division.
Both processes have the stages of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Differences
Mitosis usually lasts about an hour, while meiosis can last for days or even weeks.
In meiosis, the amount of chromosomes halves, while in mitosis, the amount of chromosomes is maintained.
Exercises
- What are gametes?
- What is the essential principal of meiosis?
- What is a haploid cell?
- How are meiosis and mitosis similar?
- How are meiosis and mitosis different?
Answers
- A gamete cell cannot develop without uniting with another cell.
- After meiosis, each cell contains just half of the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
- In haploid cells, each chromosome is unique. The chromosomes in haploid cells do not have an identical partner.
- Both processes refer to cell division and have the same stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase).
- In meiotic division, the amount of chromosomes halves, while in mitotic division, the amount of chromosomes is maintained.
You may also want to look at our posts on cellular organelles and cellular differentiation.