What are Reflexes, Synapses, and Neurotransmitters?
This page provides information about reflexes, synapses, and neurotransmitters. The explanations and examples are first. The free exercises are at the bottom of the page.
What are Reflex Actions?
Reflex actions are automatic responses within the body to external stimuli.
Reflexes are automatic in the sense that they are involuntary, and we don’t need to think about doing them.
Because we often use them in response to danger or potential injury, reflex actions are rapid responses.
What is a Reflex Arc?
The electrical impulses that are responsible for a reflex action travel along a pathway called a reflex arc.
The reflex arc pathway is as follows:
Receptors in the body transform stimuli into electrical impulses.
These nerve impulses go from the receptor and travel to a sensory neuron.
From the sensory neuron, the impulse goes to a relay neuron in the spinal cord. The impulse then goes to a motor neuron.
Finally, the impulse leaves the motor neuron and travels to an effector, where the reflex action is carried out.
What is a synapse?
A synapse is the place where two neurons join.
Remember that groups of neurons form nerves in the body.
Types of Synapses
Broadly speaking, synapses can be classified into two groups:
1) electrical synapses
2) chemical synapses
What are Electrical Synapses?
Electrical synapses pass ions and signaling molecules directly from one cell to another.
In other words, electrical synapses are a direct link between two cells in the body.
There is no synaptic delay in electrical synapses, so the response is very rapid.
What are Chemical Synapses?
No direct signal is passed between neurons in a chemical synapse.
Instead, there is a diffusion of the chemical molecules, also called neurotransmitters, in the synapse over time.
For this reason, the transmission of information via a chemical synapse is slower than that of an electrical synapse.
Remember that most synapses in the human body are chemical synapses.
How Do Chemical Synapses and Neurotransmitters Function?
When a nerve impulse travels to the end of one neuron, it creates a chemical. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters.
The chemicals are released into the gap between the neurons.
The chemicals then create an impulse in the next neuron.
This impulse continues along the reflex arc.
How Do Neurons and Synapses Work Together?
Synapses cause nerve impulses to be slowed down.
However, a neuron can form synapses with more than one neuron.
So, an impulse can pass to other neurons when it reaches the end of a sensory neuron.
Because synapses can be formed with several neurons at once, we are capable of responding to any given stimulus in more than one way.
For example, if you hear something unpleasant, you can cover your ears or walk away from the noise.
Synapses and Overriding Reflex Actions
In the spinal cord, a relay neuron forms synapses with a sensory neuron and with a motor neuron.
The spinal cord also forms synapses with neurons carrying nerve impulses from the brain.
These impulses from the brain can help you overrule a reflex action.
For instance, you may experience the reflex action of blinking when your picture is taken with a flash.
However, if you tell yourself to focus on a distant object instead of the flash, you may be able to override your reflex action and not blink.
Synapses and Neurotransmitters – Questions
1. Label the parts of a chemical synapse in the diagram below.
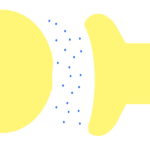
- What do the two yellow areas represent?
- What does the white gap in the middle represent?
- What do the blue dots represent?
2. How is the signal transmitted in the illustration in question 1?
3. What is the most common type of synapse in the human body?
4. A sensory neuron carries an impulse to a relay neuron in your spine, which passes it on to a motor neuron. How many synapses could be involved in this response?
5. You realize that you smell a fire in your house. Why is it advantageous that a neuron can form connections with many other neurons when you have to respond to a situation like this?
Synapses and Neurotransmitters – Answers
Answer 1
- The two yellow areas represent neurons.
- The white gap in the middle represents the synapse.
- The blue dots represent neurotransmitters.
Answer 2
The diagram in question 1 represents a chemical synapse, so no direct information is passed in this synapse.
The signal is transmitted over time from the diffusion of the chemical molecules or neurotransmitters.
Answer 3
Most synapses in the human body are chemical synapses.
Answer 4
At least three synapses could be involved in the response.
In the spinal cord, a relay neuron forms synapses with both a sensory neuron and with a motor neuron. The spinal cord also forms synapses with neurons carrying nerve impulses from the brain.
Answer 5
The presence of multiple pathways is advantageous because you can decide what action to take first. The following are among the potential actions that you could take:
- Scream “fire” to warn other members of your family
- Walk to the kitchen to see if something is burning
- Call the fire department
- Run out of the house
More help with science
For exam downloads, please click on the image below.
